We envision a world where everyone has the tools and knowledge to live a balanced, healthy, and fulfilling life. By providing reliable resources, personalized programs, and community support, we aim to be a beacon of hope for those on their health journey.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Child and Adolescent Mental Health Mind Matters
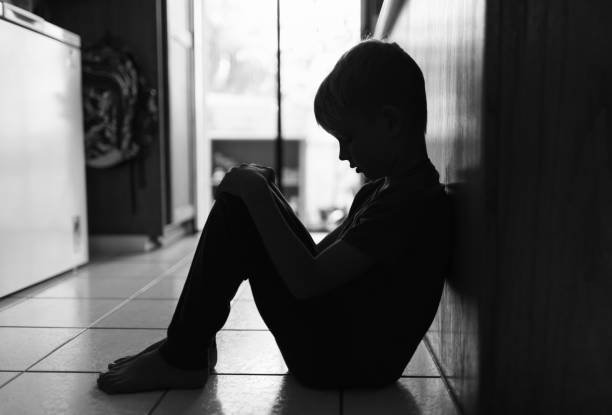
Mental health in children and adolescents is a crucial aspect of overall development that significantly influences their trajectory into adulthood. Unlike adults, children and teenagers experience a unique set of mental health challenges that are often rooted in their developmental stages and social environments. Understanding these differences is essential for fostering healthier communities. While adults may struggle with more complex issues often shaped by long-term life experiences, young individuals face mental health disorders that can disrupt their learning, relationships, and physical health at a formative time in their lives.
The prevalence of mental health disorders among children and adolescents is alarming, with estimates suggesting that about one in five young people experience a mental health issue at some point during their formative years. Disorders such as anxiety, depression, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are increasingly common, with the impacts extending beyond mental health alone. When left unaddressed, these conditions can lead to negative educational outcomes, strained relationships with family and peers, and deteriorating physical health, making it imperative to recognize and address these challenges early.
Moreover, mental health problems can manifest differently in children and adolescents compared to adults. Symptoms might be expressed through behavioral changes or reduced academic performance, which can easily be overlooked or misinterpreted. Understanding these unique manifestations is vital for parents, educators, and healthcare providers to disrupt the potential cycle of mental health issues adversely affecting the individual’s well-being and future opportunities. By prioritizing awareness and intervention in early life stages, we can enhance resilience and foster healthier developmental pathways for youth, ultimately benefiting society as a whole.
Common Mental Health Disorders in Children and Adolescents
Child and adolescent mental health disorders encompass a range of conditions that can significantly affect the emotional and behavioral functioning of young individuals. Among these, anxiety disorders are the most prevalent, affecting approximately 31.9% of adolescents aged 13-18, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Symptoms may include excessive worry, irritability, and avoidance of school or social situations. It is particularly notable that children may express anxiety differently than adults, frequently manifesting through physical complaints or behavioral regression.
Depression is another critical mental health concern, impacting about 13% of adolescents. Signs may include persistent sadness, loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities, and changes in sleep or appetite. Children are more likely to exhibit irritability and difficulty concentrating, which often differs from adult presentations of the disorder. An understanding of these distinctions is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is also common, affecting 9.4% of children in the United States. Characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness, ADHD can lead to academic challenges and strained relationships. Parents often notice struggles with organization and task completion, which can present as short attention spans and difficulty following rules. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely intervention.
Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) encompass a range of developmental conditions and affect an estimated 1 in 44 children. Symptoms can vary widely but typically include challenges in communication and social interaction, alongside repetitive behavior patterns. Young children may display an absence of social responsiveness or limited engagement in shared activities, which can be quite different from how these symptoms present in adults, who might demonstrate more overt forms of social withdrawal.
Awareness of these mental health disorders, along with signs and symptoms, is essential for parents, educators, and mental health professionals. Early identification and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for affected children and adolescents.
Risk Factors and Causes of Mental Health Issues
Mental health issues in children and adolescents can stem from a complex interplay of various risk factors, which include genetic predisposition, environmental influences, trauma, and family dynamics. Understanding these elements is essential for early intervention and effective management.
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in mental health, as many disorders have hereditary links. For instance, children with a family history of mental illnesses may be more susceptible to developing similar conditions. Studies indicate that approximately 30-40% of the variance in traits related to mental health can be attributed to genetic factors. This hereditary component underscores the importance of family assessments in identifying at-risk youth.
Environmental influences, such as socioeconomic status, community safety, and educational opportunities, also contribute to mental health outcomes. Children growing up in impoverished or unstable environments may face higher levels of stress, making them more vulnerable to mental health disorders. Research has shown that adverse socioeconomic conditions can increase the risk of anxiety and depression, indicating a strong correlation between environmental stressors and mental health issues.
Trauma is another critical factor in developing mental health disorders among younger populations. Experiencing or witnessing traumatic events, such as abuse, neglect, or loss, can have profound impacts on emotional well-being. Evidence from various studies highlights how early exposure to traumatic experiences may lead to increased rates of PTSD, depression, and anxiety disorders in both children and adolescents.
Additionally, family dynamics play a crucial role in shaping a child’s mental health. Dysfunctional family relationships, high levels of conflict, or lack of emotional support can create conditions where mental health issues may flourish. Research supports the notion that positive family interactions contribute to better mental health outcomes, signifying that nurturing home environments are essential for promoting emotional stability.
Addressing these risk factors is vital for improving mental health outcomes in youth. Awareness and understanding of the causes can guide parents, educators, and healthcare professionals in providing effective support and intervention strategies.
The Role of Family and Environment in Mental Health
The mental health of children and adolescents is profoundly influenced by their family dynamics and environmental conditions. Research indicates that parenting styles significantly shape the emotional and psychological development of young individuals. For instance, authoritative parenting, characterized by warmth and support combined with appropriate discipline, is associated with positive outcomes such as higher self-esteem and lower instances of anxiety and depression. Conversely, authoritarian parenting, which is less nurturing and more punitive, can lead to increased behavioral issues and mental health challenges in children.
Socioeconomic status is another critical component that affects mental health. Children from lower socioeconomic backgrounds often encounter heightened levels of stress due to financial strain, unstable housing, and limited access to quality healthcare and education. According to a study by the National Institute of Mental Health, children from low-income families are at higher risk for developing anxiety and mood disorders. Additionally, socioeconomic factors can limit access to community resources, such as counseling and after-school programs, which play crucial roles in promoting mental well-being.
Furthermore, the environment in which a child grows up also impacts their mental health. Communities with high levels of violence, crime, and drug use can create a culture of fear and stress, which adversely affects young people’s mental health. In contrast, communities that offer strong support networks, recreational activities, and educational resources can contribute positively to the mental well-being of children and adolescents. Evidence from the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry suggests that community cohesion and supportive relationships with peers and adults can counteract adverse experiences, thereby fostering resilience in young people.
To fully understand the complexity of mental health in children and adolescents, it is essential to consider these familial and environmental factors. By addressing the various influences on mental health, families and communities can create supportive environments that nurture the psychological well-being of younger generations.
Signs and Symptoms: How to Recognize Mental Health Issues
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of mental health disorders in children and adolescents is crucial for effective intervention. Early detection can significantly improve outcomes, allowing for timely support and appropriate treatment. Mental health issues may manifest differently in younger populations, making awareness paramount for parents, educators, and caregivers. Below are some common symptoms to look for:
- Changes in Mood: Persistent sadness, irritability, or mood swings that seem out of the ordinary.
- Withdrawal: A noticeable withdrawal from family, friends, or previously enjoyed activities.
- Changes in Appetite: Significant increase or decrease in eating habits, or complaints about stomachaches without medical cause.
- Sleep Disturbances: Trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing nightmares regularly.
- Academic Decline: Deterioration in academic performance, lack of concentration, or a sudden drop in grades.
- Behavioral Issues: Increased aggression, defiance, or a drop in self-control accompanied by outbursts.
- Physical Symptoms: Frequent headaches, fatigue, or other unexplained physical complaints.
- Fearfulness: Excessive worries or fears that seem to interfere with day-to-day activities.
Identifying these symptoms early can provide critical insight into a child’s mental well-being. It’s worth noting that the presence of one or more of these signs does not automatically indicate a psychiatric disorder; however, they should serve as red flags prompting further investigation. Parents and educators can use various self-assessment tools available online to help evaluate mental health in children and adolescents. Initiating conversations about mental health, fostering open communication, and encouraging children to express their feelings can also be vital in addressing these concerns. If any of the aforementioned signs persist or worsen, consulting with a mental health professional is advisable. Early engagement not only promotes understanding but can also facilitate the path to recovery and improved resilience.
The Importance of Professional Help and Therapy Options
Addressing child and adolescent mental health is crucial for the overall development and well-being of young individuals. Professional help can significantly contribute to managing various mental health challenges they may face. Different types of mental health professionals, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, and counselors, each play vital roles in providing support tailored to specific needs.
Pediatric psychologists specialize in diagnosing and treating emotional, behavioral, and developmental issues. They often employ evidence-based techniques, such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. This method is particularly effective for anxiety and mood disorders in children and teenagers. Psychiatrists, on the other hand, are medical doctors who can prescribe medications in conjunction with therapy, which may be necessary for managing more severe conditions like depression or ADHD.
Counselors are also important figures in the realm of mental health; they offer guidance and support through talk therapy and can address various life challenges, such as peer pressure, family issues, or school-related stress. In some cases, creative methods like Play Therapy may be used, especially with younger children who may find it difficult to express their feelings verbally. This approach allows children to communicate through play, offering them a safe space to explore their emotions.
Early intervention is crucial in mitigating long-term psychological issues. Seeking help at the earliest signs of distress can lead to healthier coping mechanisms and improved outcomes. Parents and guardians can initiate this process by reaching out to local mental health services or helplines, which provide resources and referrals to qualified professionals. National hotlines, like the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline, can offer support and guidance in urgent situations while directing families to nearby mental health facilities.
Promoting Mental Well-being: Strategies for Parents and Educators
Encouraging mental well-being in children and adolescents is a vital responsibility for both parents and educators. By fostering a supportive environment, adults can significantly impact the emotional and mental health of young individuals. One of the foundational strategies is to cultivate healthy communication. Open dialogues about feelings, thoughts, and experiences can help children articulate their emotions more effectively. Parents and educators should create safe spaces where youngsters feel comfortable expressing themselves without the fear of judgment.
Physical activity also plays a pivotal role in promoting mental health. Encouraging regular participation in sports, outdoor play, or physical exercise can greatly enhance mood and reduce anxiety. Parents might collaborate with schools to incorporate systematic physical activity programs that cater to all age groups. Seeking local community resources, such as youth sports leagues, can also provide additional support. For a comprehensive guide on physical activities that benefit mental health, refer to our resource on engaging physical activities for youth.
Another crucial aspect is building resilience. Teaching children coping mechanisms to deal with life’s challenges fosters a sense of independence and confidence. Techniques such as problem-solving skills, goal-setting, and positive thinking should be imparted early on. Workshops and seminars on resilience-building for both parents and educators can be useful tools, and links to accessible programs can be found on our page dedicated to resilience in youth.
To sum up, fostering mental well-being requires consistent efforts from both parents and educators. With effective communication, encouragement of physical activity, and the development of resilience, adults can support the mental health of young individuals. Utilizing these strategies can pave the way for a healthier, more balanced lifestyle for children and adolescents, ensuring a brighter future in terms of mental health.
School’s Role in Supporting Mental Health
Schools play a pivotal role in the mental health landscape of children and adolescents. As a primary environment where children spend a significant portion of their time, educational institutions are uniquely positioned to identify and address mental health needs. Early intervention can dramatically alter a student’s academic trajectory, making it essential for schools to implement effective programs and policies aimed at mental well-being.
One effective approach is the establishment of comprehensive mental-health programs that include counseling services, mental-health education, and support groups. These programs empower students and provide them with tools to manage their emotional well-being. For instance, initiatives like peer support programs can foster a culture of empathy and understanding among students, while workshops can educate them about mental-health issues, helping to reduce stigma. Furthermore, integrating mental-health into the curriculum can raise awareness and normalize discussions surrounding mental-health challenges.
Moreover, the success of such programs heavily relies on well-trained educators. Teacher training programs should include components focused on recognizing the signs of mental-health issues such as anxiety and depression. When teachers are equipped with this knowledge, they can intervene early, connect students with the necessary support services, and create a supportive environment conducive to learning. This could involve specialized training sessions or partnerships with mental-health professionals to enhance teachers’ understanding.
Several schools have successfully implemented these strategies. For example, the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) promotes evidence-based programs focusing on social-emotional learning (SEL) that have been proven to increase students’ coping skills and academic performance. In conclusion, the critical role of schools in supporting child and adolescent mental-health cannot be overstated, as they provide the foundation for proactive support systems aimed at fostering students’ overall well-being.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In addressing the significant subject of child and adolescent mental-health, we have explored the various dimensions and factors that influence emotional well-being in young individuals. Recognizing the prevalence of mental-health issues among children and adolescents is crucial, as these challenges can impact their daily lives, academic performance, and social interactions. Early intervention and support can play a vital role in mitigating the long-term effects of mental-health disorders, making awareness and education essential components in this domain.
This guide has outlined the importance of identifying symptoms and understanding the various approaches to mental-health care. It has emphasized that mental wellness is not merely the absence of illness but a state of overall well-being. Families must engage in open communication regarding mental health, fostering an environment where children feel safe to express their emotions and concerns. These discussions can demystify mental-health, reduce stigma, and encourage a proactive approach to seeking help.
It is essential to remember that reaching out for help is not a sign of weakness but an important step toward healing. Parents, caregivers, and guardians are encouraged to remain vigilant, recognizing when a child may need additional support. Resources are available, including counseling services, support groups, and educational programs designed to assist families in navigating these complex issues.
Therefore, we urge readers to engage in conversations about mental health within their families. Explore the resources available to you—consider visiting local links dedicated to mental health support and community services. By prioritizing mental-health and encouraging open dialogue, we can create a more informed and supportive environment for our children.