We envision a world where everyone has the tools and knowledge to live a balanced, healthy, and fulfilling life. By providing reliable resources, personalized programs, and community support, we aim to be a beacon of hope for those on their health journey.
Table of Contents
Understanding Stress and Its Sources; Work Stress
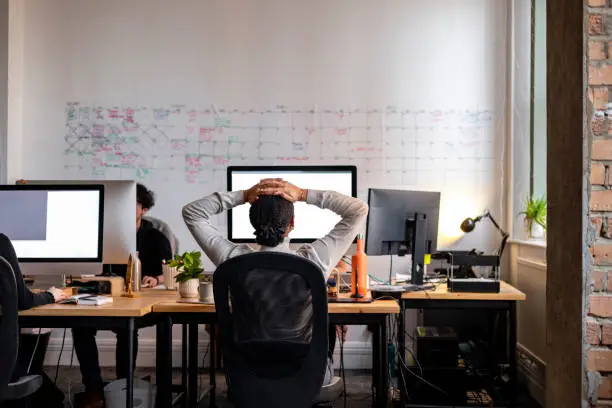
Stress is a universal experience characterized by a range of emotional, physical, and behavioral responses to perceived challenges or threats. It can be classified into two primary categories: acute stress and chronic stress. Acute stress is a short-term response to immediate pressures, such as meeting a project deadline or preparing for a presentation. It often resolves once the stressful situation has passed. In contrast, chronic stress is a prolonged form that arises from ongoing situations, such as a demanding job, which can lead to serious health issues if not managed effectively.
Work-related stressors can take many forms. Common sources include stringent deadlines, excessive workloads, and unclear job expectations. These elements often create an environment where employees feel overwhelmed and unable to perform effectively. Additionally, workplace dynamics, such as poor relationships with colleagues, lack of support from management, and job insecurity, can further exacerbate stress levels. Research indicates that a negative workplace atmosphere, characterized by hostility or competition instead of collaboration, can significantly impact mental health and productivity.
Recognizing personal stress triggers is vital for managing stress effectively. Triggers may vary significantly from one individual to another; what instigates stress for one person might not have the same effect on another. Therefore, self-awareness plays a crucial role in attending to signs of stress early. Furthermore, the culture within a workplace can influence how stress is experienced. A positive organizational culture that encourages open communication and provides support can mitigate stress levels, while a toxic environment can intensify them.
For further reading on stress psychology, reputable sources such as the American Psychological Association offer valuable insights into the complexities of stress, its sources, and strategies for coping and resilience.
The Connection Between Work and Mental Health
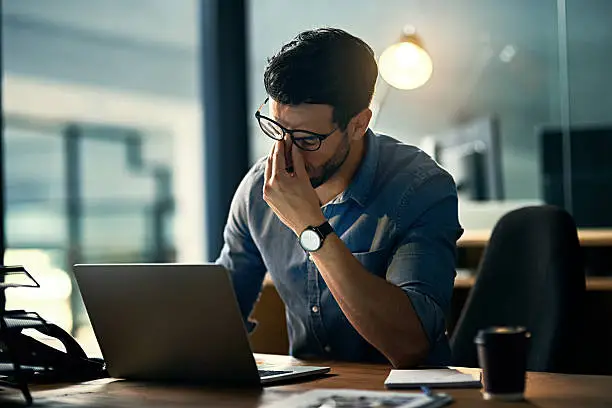

Work-related stress is a significant factor influencing mental health, as individuals often face high demands combined with tight deadlines, limited resources, and escalating pressures. This combination can lead to psychological disorders, most notably anxiety, depression, and burnout. The World Health Organization identifies these mental health issues as critical public health challenges, affecting employees across various sectors. Importantly, studies have indicated that workers in high-stress environments experience increased rates of these conditions.
Research consistently demonstrates a strong correlation between job stress and mental health disorders. A recent study found that approximately 60% of workers in high-stress jobs reported symptoms of anxiety, compared to only 30% in lower-stress positions. Additionally, the prevalence of depression among those working in high-stress roles is notably higher. It is essential for organizations to recognize that such mental health issues can lead to decreased productivity and increased absenteeism, ultimately impacting the workplace culture.
Burnout, a syndrome characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced personal accomplishment, is increasingly recognized as a consequence of chronic work-related stress. Data indicates that burnout rates are alarmingly high, with nearly 50% of employees in demanding jobs reporting feelings of burnout. Burnout not only affects individual employees but can also permeate organizations, leading to higher turnover rates and decreased overall performance.
Statistics reveal a concerning landscape for mental health in the workforce. A survey indicated that nearly one in four employees experience some form of mental health disorder, highlighting the urgent need for companies to address mental wellness initiatives. By integrating supportive practices and resources, employers can help mitigate stress and enhance mental health outcomes, ultimately creating a healthier work environment that prioritizes employee well-being.
Identifying Symptoms of Stress-Related Mental Health Issues
Understanding the symptoms associated with stress-related mental health issues is essential for early recognition and intervention. Stress can have profound effects on emotional, cognitive, physical, and behavioral health. Each of these domains may exhibit specific symptoms that can provide insights into an individual’s mental well-being.
Emotionally, individuals experiencing stress may encounter feelings of anxiety, irritability, or an overall sense of unease. These emotional symptoms can manifest as mood swings, excessive worry, or difficulty concentrating. Such feelings can interfere with daily activities and diminish overall productivity. Additionally, a pervasive sense of sadness or hopelessness may emerge as stress accumulates.
Cognitive symptoms of stress may include memory problems, indecisiveness, or difficulty with focusing. These cognitive challenges can hinder problem-solving abilities and affect performance at work or in personal life. As stress grips an individual, racing thoughts or persistent fears about various aspects of life can further complicate an already taxing mental landscape.
On a physical level, stress may present with symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, or gastrointestinal issues. These physical manifestations can be indicative of the body’s response to stress, as chronic tension can lead to muscle pain or disrupt sleep patterns, contributing to a cycle of fatigue and increased stress levels.
Behavioral signs can also emerge, including changes in eating patterns, withdrawal from social engagements, or increase in substance use. Individuals may also exhibit decreased motivation and productivity, leading to further stress and a negative feedback loop. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for both individuals and those around them, enabling timely responses and access to appropriate mental health resources.
For further assistance, individuals can explore mental health resources and screening tools available online that provide additional support and guidance in managing stress and its ramifications on mental well-being.
The Role of Workplace Environment in Mental Health

The workplace environment plays a crucial role in shaping employees’ mental health. Numerous factors, including management style, peer relationships, and organizational culture, significantly impact how individuals feel and perform at work. A positive workplace environment fosters mental well-being, while a toxic atmosphere can contribute to stress and related mental health issues.
Management style is one of the most influential aspects of the workplace environment. Effective leaders who adopt a supportive, inclusive approach can significantly enhance employees’ mental health. They promote open communication, provide constructive feedback, and encourage a healthy work-life balance. Conversely, authoritarian management styles, characterized by rigid hierarchy and lack of empathy, can lead to a stressful environment where employees feel undervalued and overwhelmed. Such conditions may exacerbate mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Peer relationships also play a vital role in mental health within the workplace. Positive interactions among colleagues can create a sense of belonging and support, which is essential for mental well-being. Teamwork and camaraderie can provide employees with emotional resilience during challenging times. On the other hand, negative peer interactions, such as bullying or social isolation, can lead to a decline in mental health, further emphasizing the need for organizations to cultivate a respectful and collaborative atmosphere.
Organizational culture acts as the framework that defines how employees interact, including shared values and expectations. A culture that prioritizes mental health by offering resources like counseling and workshops can empower individuals to seek help when needed. Additionally, promoting a culture of flexibility, where employees can adjust their schedules to maintain a healthy balance, can lead to improved mental health outcomes. By investing in a positive workplace environment, organizations not only enhance employee satisfaction but also drive better performance and retention rates.
Coping Strategies for Stress Management at Work
Managing stress in the workplace is essential for maintaining mental health and overall well-being. Employees can adopt various coping strategies to mitigate stress effectively while improving their work efficiency. One crucial technique is effective time management. By prioritizing tasks and setting realistic deadlines, employees can reduce overwhelming feelings associated with tight schedules. Utilizing tools such as calendars and to-do lists can provide structure and clarity, allowing individuals to focus on completing tasks methodically.
Mindfulness practices are another powerful approach for stress reduction in the work environment. Engaging in short mindfulness exercises, such as deep breathing or brief meditation, can create a significant shift in mental state, helping employees to stay grounded and present in their tasks. work Stress; Implementing these practices into daily routines can bolster resilience against stressors that arise during working hours.
The importance of taking regular breaks cannot be overstated. Short intervals of rest throughout the day can rejuvenate employees, preventing burnout and enhancing productivity. Activities such as stretching, taking a walk, or simply stepping away from one’s workstation for a moment can provide necessary mental reprieve, facilitating a clearer mindset upon return to tasks.
Moreover, fostering open communication and establishing a supportive environment among colleagues can significantly alleviate workplace stress & work Stress . Sharing concerns and discussing challenges with peers not only promotes a sense of belonging but also enables team members to collaboratively find solutions. Organizations can further encourage this camaraderie by offering stress-reducing programs or initiatives, which can be instrumental in building a culture of well-being.
Incorporating these strategies can empower employees to manage stress effectively at work, ultimately contributing to a healthier workplace environment. For additional insights on stress-reducing techniques or programs offered by employers, consider exploring linked articles that delve deeper into these topics.
Seeking Professional Help: When and How
In the context of stress & work Stress and its impact on mental health, seeking professional help can be a pivotal step for those experiencing overwhelming challenges. Recognizing when to consult a mental health professional can significantly influence one’s journey towards recovery and well-being. Symptoms such as persistent anxiety, emotional distress, and an inability to cope with daily responsibilities may indicate the need for assistance. Furthermore, if stress leads to physical symptoms, such as headaches or fatigue, it is advisable to consider professional help promptly.
When contemplating therapy, understanding the diverse options available can guide individuals toward the best fit for their needs. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is particularly effective for stress & work Stress management, as it assists individuals in identifying and altering negative thought patterns. Other forms of therapy, such as mindfulness-based therapy or psychodynamic therapy, can also provide significant benefits depending on personal preference and specific issues faced.
For those in a workplace setting, it is important to explore company-sponsored health services. Many organizations offer employee assistance programs (EAPs) that provide employees with access to counseling services, stress management workshops, and wellness resources at no additional cost. Utilizing these services can promote a healthier workplace culture and support mental wellness in high-stress & work Stress environments.
Finding the right therapist or mental health service can indeed feel daunting. A good starting point is to consult reputable mental health organizations or online directories, which often provide lists of qualified professionals. Websites like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) and the American Psychological Association (APA) offer directories that allow individuals to search for mental health providers based on specialized treatment areas, geographical location, and accepted insurance plans.
In summary, acknowledging the need for professional help is a courageous and vital step towards addressing stress-related mental health issues. work Stress; By utilizing both therapy options and workplace resources, individuals can improve their mental health and overall quality of life.
Creating a Healthy Work-Life Balance
In today’s fast-paced world, the significance of establishing a healthy work-life balance cannot be overstated. This balance is vital in mitigating stress & work Stress; and enhancing mental well-being, as prolonged work-related stress can have detrimental effects on an individual’s health. One of the primary strategies for achieving this balance is to set clear boundaries between work and personal life. This may involve designating specific work hours, creating a dedicated workspace at home, and communicating these boundaries to colleagues and family members. By delineating these lines, individuals can create a more structured environment that supports both professional obligations and personal fulfillment.
Prioritizing self-care is another crucial component of achieving a healthy work-life balance. Engaging in activities that promote physical and mental wellness, such as exercise, mindfulness practices, or hobbies, allows individuals to recharge. Allocating time for relaxation and leisure not only reduces stress & work Stress but also enhances productivity at work. work Stress; Therefore, scheduling regular breaks, taking vacations, and ensuring that weekends are free from work-related tasks are important practices to incorporate into one’s routine.
Effective time management skills also play a vital role in maintaining this equilibrium. Individuals should consider utilizing prioritization techniques, such as the Eisenhower Box, which distinguishes between what is urgent and important. work Stress; By prioritizing tasks, one can focus on completing critical issues first, thus reducing unnecessary pressure and extending free time for other activities. work Stress; Furthermore, employing digital tools and apps can assist in organizing tasks and deadlines, contributing to a more manageable workflow.
Instructing oneself to recognize the signs of burnout ensures timely intervention. Seeking support from supervisors, mentors, or mental health professionals should not be overlooked. Ultimately, fostering a healthy work-life balance contributes significantly to lowering stress & work Stress levels, thereby nurturing overall mental health.
Employer Responsibilities for Employee Mental Health
In contemporary work environments, the psychological well-being of employees is paramount, placing significant responsibility on employers to foster mental health within the workplace. Employers are expected to take an active role in promoting mental health initiatives, which not only enhance employee morale but also boost overall productivity. work Stress; A comprehensive approach to mental health can include implementing robust workplace policies, creating accessible resources, and fostering a supportive company culture.
One key responsibility for employers is to establish clear mental health policies that outline expectations, support mechanisms, and procedures for discussing mental health issues. Such policies should include provisions for mental health days, well-being programs, and access to mental health professionals. For instance, according to the World Health Organization, every dollar invested in mental health treatment work Stress yields a return of four dollars in improved health and productivity. This statistic highlights the tangible benefits of prioritizing mental health resources.
Moreover, employers can enhance support for their employees by offering training for managers on how to recognize and respond to mental health concerns. work Stress; This is crucial as the role of leadership is vital in shaping workplace culture. Workplaces that promote a culture of openness and understanding tend to see higher engagement levels and lower absenteeism rates. work Stress; Furthermore, initiatives such as Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) can provide confidential counseling services, allowing employees to address mental health issues discreetly.
Being proactive regarding employee mental health is not merely a legal or moral obligation; it is a strategic investment. By cultivating an environment that values mental well-being, employers can enhance not just individual health, but also the overall health of the organization. work Stress; Building a mentally healthy workplace ensures that employees feel valued and supported, ultimately leading to improved job satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion: Taking Action for Better Mental Health

In concluding our exploration of the impact of stress and work on mental health, it is crucial to recognize the significant role that both employees and employers play in addressing this pressing issue. The relationship between work stress and mental well-being cannot be overstated; it demands our immediate attention and action. work Stress; Employees may experience a range of challenges, from burnout to anxiety, while employers face the repercussions of decreased productivity and higher turnover rates, indicating the need for a comprehensive approach to mental health at work Stress.
To foster a healthier workplace Work Stress; environment, several actionable steps can be implemented. Employers should consider establishing stress management programs, promoting regular breaks, and encouraging a culture of openness where mental health issues can be discussed without stigma. Providing resources such as access to counseling services or wellness initiatives can empower employees to seek help proactively. Work Stress; Furthermore, training managers to recognize signs of stress in their teams can facilitate early intervention and support.
On the other hand, employees should also take proactive steps towards managing their mental health. Work Stress; Techniques such as mindfulness, time management, and developing a support network among colleagues can create a buffer against work stress. It is essential for individuals to prioritize self-care and be aware of their mental health needs, recognizing when to reach out for professional guidance.
Engagement within the workplace community can also be valuable. Readers are encouraged to share their experiences or resources that have helped them manage stress effectively. Work Stress; By fostering an environment where individuals feel comfortable discussing their challenges and strategies, we can collectively work towards a healthier and more supportive workplace culture. Work Stress; Remember, prioritizing mental health is not just a personal responsibility; it is a fundamental component of a thriving work environment.