We envision a world where everyone has the tools and knowledge to live a balanced, healthy, and fulfilling life. By providing reliable resources, personalized programs, and community support, we aim to be a beacon of hope for those on their health journey.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Skin Cancer
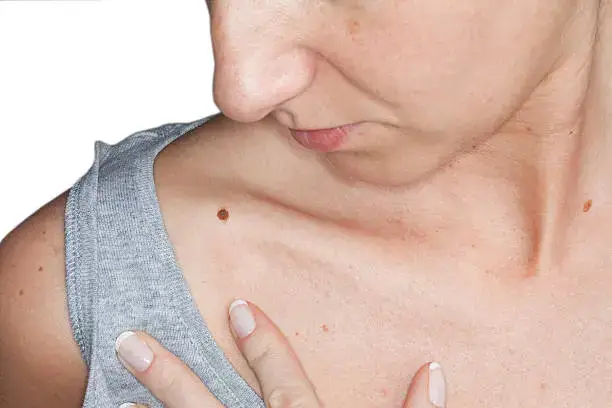
skin cancer symptoms
Skin cancer is recognized as one of the most prevalent forms of cancer globally, affecting millions of individuals each year. It arises when skin cells begin to grow uncontrollably due to damaged DNA, often as a result of excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation exposure from sunlight or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Understanding the different types of skin cancer, including Melanoma Skin Cancer, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, is crucial. Each type varies significantly in terms of severity, growth patterns, and treatment options.
The most common skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma, usually manifests as a small, shiny bump, primarily on sun-exposed areas, while squamous cell carcinoma often appears as red, scaly patches or sores. Melanoma, though less common, represents the most dangerous form of skin cancer due to its ability to metastasize rapidly if left untreated. The importance of recognizing symptoms early cannot be overstated, as timely detection is crucial to effective treatment and favorable outcomes.
Several risk factors elevate an individual’s chance of developing skin cancer. These include having a lighter skin type, a family history of skin cancer, exposure to UV radiation, and a history of sunburns, especially during childhood. Additionally, certain medical conditions and immunosuppressive medications may increase susceptibility to skin malignancies. It is critical for everyone, regardless of skin type or tone, to engage in preventive measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and conducting regular skin self-examinations to identify any unusual changes early. Understanding these aspects integrates into a broader strategy for skin health and fosters a proactive approach toward preventing and managing skin cancer effectively.
The Different Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a pressing health concern that arises from the abnormal growth of skin cells, and understanding its different types is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. The three primary types of skin cancer are melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, each exhibiting distinct features and symptoms.
Melanoma is recognized as the most aggressive form of skin cancer, originating from melanocytes—the cells responsible for pigment production. Symptoms of melanoma often appear as irregular moles or growths that may display asymmetry, irregular borders, varied colors, or changes in size. Early detection significantly increases the chances of successful treatment, emphasizing the need for individuals to routinely check their skin for any changes.
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer, usually developing in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face and neck. Symptoms may include a small, pearly bump, flat scar-like lesion, or reddish, irritated patches. BCC tends to grow slowly and often does not spread to other parts of the body, making it vital to address any suspicious spots promptly, as untreated BCC can lead to significant local damage.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is another form of skin cancer that arises from squamous cells, which are found in the outer layer of the skin. Symptoms may include a firm, red nodule, a flat sore that bleeds or crusts over, or a new growth that appears similar to a wart. SCC can also be triggered by prolonged sun exposure and tends to grow more rapidly than BCC, highlighting the importance of early assessment.
Recognizing these different types of skin cancer and their respective symptoms is invaluable for ensuring timely medical intervention. Awareness of the variations can lead to early detection, which is essential for successful treatment outcomes.
Common Symptoms of Skin Cancer
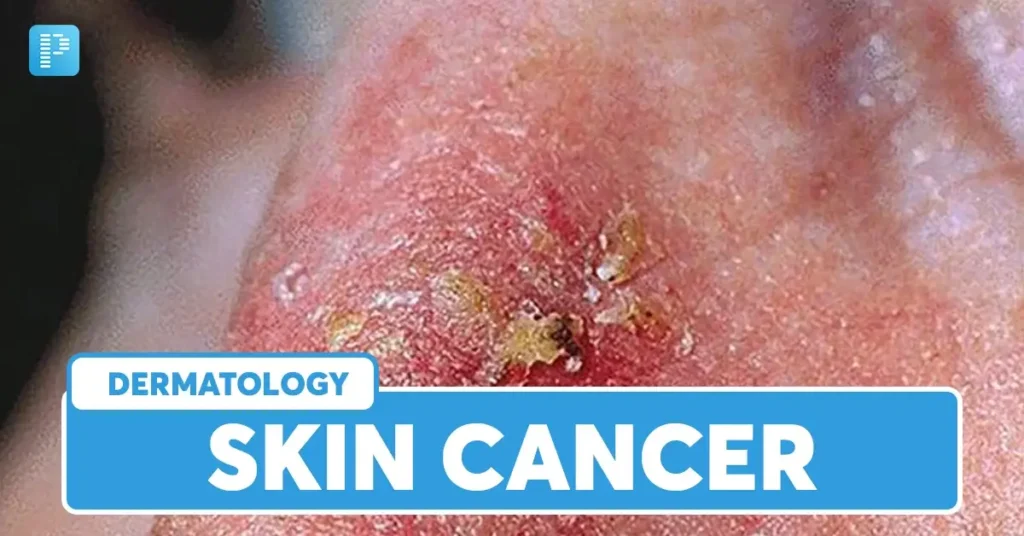
Skin cancer, which manifests in various forms, often presents noticeable changes in the skin. One of the most common symptoms to watch for is the alteration of existing moles or spots. This can include changes in size, shape, color, or texture. For instance, if a mole becomes asymmetrical or if its borders become irregular, these may be signs of a malignant transformation. Furthermore, a mole that gradually darkens or develops multiple colors may warrant further examination.
Another symptom to be aware of is the emergence of new growths on the skin. These growths can take several forms, including small lumps, nodules, or flat lesions that may be reddish or scaly in appearance. Notably, the popularity of self-skin examinations should not be underestimated, as early detection significantly enhances the effectiveness of treatment options available for these new formations.
Unusual skin lesions also represent a significant indicator of possible skin cancer. These can present as patches of skin that are itchy, bleeding, or are not healing as expected. Such lesions may vary in color from pink to brown and can exhibit a shiny, waxy, or scaly texture. Importantly, any persistent changes in the skin, particularly those that do not resolve over time, should prompt an immediate consultation with a healthcare provider.
The diverse manifestations of skin cancer highlight the importance of vigilance regarding one’s skin condition. Regular check-ups, coupled with proactive self-assessments, can aid in the early identification of these symptomatic changes. Awareness of these signs is critical, as they play an essential role in the timely diagnosis and management of skin cancer, ultimately contributing to more favorable health outcomes.
The ABCDE Rule for Skin Cancer Detection
The ABCDE rule is a widely accepted guideline that aids individuals in identifying potential melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer. Each letter in the acronym represents a specific characteristic of moles and skin lesions that one should examine carefully. Understanding these factors can empower people to take proactive steps regarding their skin health.
A for Asymmetry: This component refers to the shape of a mole or lesion. If you draw a line through the middle of the mole and the two halves do not match, it is asymmetrical. Asymmetry can be a warning sign of melanoma. For example, if one half of a mole has a different shape or size compared to the other, this could indicate potential malignancy.
B for Border: The border of a healthy mole is typically smooth and even. In contrast, moles that have irregular, jagged, or scalloped edges may raise concerns. An uneven border could suggest a developing skin cancer, warranting further examination. Individuals should observe if the edges of a mole are blurred or not clearly defined.
C for Color: A mole or lesion that displays a variety of colors—such as brown, tan, black, red, white, or blue—may be indicative of melanoma. A uniform color is generally associated with benign moles. Any noticeable variations in color should prompt further assessment by a healthcare professional.
D for Diameter: The diameter of a mole is also an essential factor in detecting potential skin cancer. Moles that are larger than a quarter of an inch (about 6 mm) may warrant concern, though some melanomas can be smaller. Regular self-examinations can help individuals track any changes in size.
E for Evolving: Moles that change in texture, color, size, or shape should be monitored closely. An evolving mole can be an early indicator of melanoma. Changes may occur over weeks or months, so maintaining awareness of any alterations is crucial for early detection and treatment.
By using the ABCDE rule, individuals can play a proactive role in monitoring their skin for potential signs of melanoma. Regular skin checks and consultations with a dermatologist can significantly reduce the risks associated with late-stage skin cancer diagnoses.
When to See a Doctor
Recognizing the signs of skin cancer is crucial for early intervention and treatment. It is imperative to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any significant changes in your skin. One key factor to consider is the duration of symptoms. If any alterations—such as new growths, moles, or discolorations—persist for more than a few weeks, it is advisable to seek medical attention. Prolonged changes can be indicative of underlying issues that may require further evaluation.
Changes in the appearance of existing moles or skin lesions should also provoke concern. Specifically, if a mole becomes asymmetrical, has irregular borders, exhibits color variations, or increases in diameter, it is essential to schedule an appointment with a dermatologist. The “ABCDE” rule is a useful guideline: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter larger than 6mm, and Evolving shape or size are characteristics that warrant examination. Early detection increases the likelihood of successful treatment and improved outcomes.
Additionally, personal and family history plays a significant role in assessing risk. Individuals with a personal history of skin cancer or those with close relatives who have been diagnosed should maintain a vigilant approach to skin changes. Genetic predisposition can heighten the risk of developing skin cancer, making it crucial for those at elevated risk to seek periodic check-ups and expert advice. Furthermore, frequent visits to a healthcare professional are advisable if there is a history of excessive sun exposure, the use of tanning beds, or a compromised immune system.
In conclusion, being proactive about your skin health is essential. If you notice prolonged skin changes, alterations in existing lesions, or have a heightened risk due to your medical background, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection is key in effectively managing skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors associated with skin cancer is essential for prevention and early detection. Several elements can heighten an individual’s susceptibility to developing this condition, and recognizing these factors can lead to more informed lifestyle choices. One of the primary risk factors is genetics; having a family history of skin cancer can significantly increase the likelihood of an individual also developing the disease. Studies suggest that specific genes may predispose individuals to skin cancer, including those with a hereditary condition known as xeroderma pigmentosum, which impairs the skin’s ability to repair UV-induced DNA damage.
Another critical aspect is skin type. Individuals with fair skin, light-colored eyes, and red or blonde hair represent a higher risk group as they have less melanin, the pigment that provides some protection against UV radiation. People with freckles are also at an increased risk. Sun exposure is another significant contributor; prolonged and unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun can cause skin damage over time, leading to mutations that may result in skin cancer.
Additionally, the use of tanning beds poses a notable risk. These devices emit UV radiation, which can be just as harmful as sun exposure, increasing the risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. Furthermore, geographical location plays a role; individuals living in areas with high sun exposure, such as those closer to the equator, experience higher levels of ultraviolet radiation, contributing to increased risk. Other factors, such as age and weakened immune systems, can also influence the likelihood of developing skin cancer. Therefore, understanding these risk factors is vital for individuals to take preventive measures and seek regular skin evaluations.
Protecting Your Skin from Cancer

Protecting your skin from cancer is an essential aspect of overall health and well-being. Skin cancer, primarily caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, can be mitigated through several preventive strategies. One of the most effective measures is the consistent and proper application of broad-spectrum sunscreen. This type of sunscreen guards against both UVA and UVB rays, which are known contributors to skin damage and cancer. It is critical to choose a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 and to apply it generously to all exposed skin, reapplying every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
In addition to sunscreen, wearing protective clothing is another vital strategy in skin cancer prevention. Fabrics that are tightly woven, dark-colored, and long-sleeved can offer an extra layer of defense against harmful UV rays. Hats with wide brims can shield the face, neck, and ears—areas particularly susceptible to sun damage. Additionally, seeking shade during peak sun hours, typically from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., can significantly reduce UV exposure.
Avoiding tanning beds is another critical step. These artificial sources of UV radiation have been linked to an increased risk of skin cancer, particularly in young individuals. Instead of tanning beds, consider safer alternatives for achieving a bronzed appearance, such as self-tanning lotions or sprays, which do not pose a risk to skin health.
Regular skin examinations are also integral to cancer prevention. Individuals should perform self-examinations to identify any changes in their skin, such as new moles or alterations to existing ones. Dermatologists recommend that adults have professional skin checks at least once a year. Early detection of any anomalies can lead to more effective treatment outcomes. By adopting these preventive measures and maintaining regular skin examinations, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing skin cancer.
Myths and Misconceptions about Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a serious health concern that has been often misunderstood. Numerous myths and misconceptions surrounding its causes and symptoms can lead to misinformation and potentially hazardous behaviors. One prevalent myth is the belief that individuals with darker skin tones are immune to skin cancer. While it is true that darker-skinned individuals have a lower risk of developing certain types of skin cancer, such as melanoma, they are still susceptible to the disease. This misconception can lead to neglecting sun protection measures and regular skin check-ups, as individuals may underestimate their risk.
Another common misunderstanding pertains to tanning. Some people believe that tanning—whether through sun exposure or tanning beds—provides protection against skin cancer. However, any change in skin color due to tanning reflects skin damage, increasing the risk of skin cancer. It is crucial to recognize that there is no safe tanning method; both natural sunlight and artificial UV light can cause DNA damage to skin cells, leading to mutations that may result in cancer. Therefore, maintaining healthy skin involves avoiding tanning altogether.
Moreover, many assume that skin cancer can only develop in areas that have suffered from severe sunburns. While sunburns are indeed a risk factor, skin cancer can appear in areas that have never been sunburned or even exposed to sunlight. For instance, melanomas can occur in less visible areas, such as the soles of the feet, under fingernails, or in the mucous membranes. Educating oneself about skin cancer entails recognizing that it can affect anyone, regardless of skin type or history of sunburns. This expanded understanding is essential in fostering timely detection and effective prevention strategies for skin cancer.
Conclusion and Encouragement for Early Detection
In conclusion, understanding skin cancer symptoms is paramount for effective early detection and treatment. Throughout this guide, we have discussed the various forms of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. Each type possesses distinct characteristics and potential warning signs, underscoring the importance of being proactive in monitoring skin health.
Being vigilant about changes in your skin can significantly improve treatment outcomes. It is essential that individuals regularly check their skin for new growths, changes in existing moles, or any unusual markings. Maintaining a system of self-examinations can serve as a first line of defense against skin cancer. Recognizing symptoms early can lead to timely diagnosis and intervention, which can be critical in managing the disease effectively.
Additionally, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist at least annually, or more frequently if you have a history of skin cancer or are at heightened risk due to factors such as fair skin, excessive sun exposure, or a family history of the disease. These professionals can provide invaluable guidance, education, and necessary screenings that contribute to early detection.
Moreover, adopting sun-safe practices—such as wearing sunscreen, seeking shade, and avoiding tanning beds—can further help mitigate your risk of developing skin cancer. Encouraging family and friends to engage in their regular skin checks can foster a community approach to early detection. Together, we can create a culture of awareness and vigilance regarding skin health, ultimately enhancing our chances of walking the path toward recovery should skin cancer arise.
blood work brain health climate health diabetes treatments digestive health disease management disease mapping exercise plan fitness tips hair care hair growth hair treatment headache treatment health care health expenses health foods health insurance health secrets health tips healthy alternatives healthy habits healthy recipes heart health home workouts immune boost immune foods keto delivery lifestyle diseases medicine innovation mental health morning exercise natural remedies non melanoma nutritional advice raw nutrition skin cancer skin care skin health sleep exercise sleep technology telemedicine services unhealthy habits viral threats walking benefits weight loss