Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
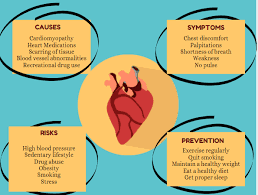

Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is a critical medical condition characterized by an abrupt loss of heart function, leading to an immediate cessation of blood flow to the brain and other vital organs. This phenomenon occurs due to the heart’s inability to effectively pump blood, often caused by electrical disturbances within the heart. These disturbances can lead to arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation, where the heart’s electrical signals become chaotic, preventing it from contracting properly. It is crucial to distinguish sudden cardiac arrest from a heart attack.
The prevalence of sudden cardiac arrest in the general population is noteworthy. According to estimates, approximately 356,000 cases of out-of-hospital cardiac arrests occur annually in the United States alone, with survival rates being frighteningly low, often less than 10%. High-risk populations include those with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions, history of heart attacks, or other risk factors such as obesity, smoking, and genetics. Immediate intervention, typically involving cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation, is vital to increase the chances of survival, as every passing minute without treatment diminishes the likelihood of a successful recovery.
The gravity of sudden cardiac arrest necessitates increased awareness and preparedness among the public, with initiatives for training in CPR and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs). Such measures can turn bystanders into lifesavers, significantly impacting outcomes in situations where every second counts.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is a critical medical condition characterized by the abrupt cessation of heart function. Among the various underlying heart conditions, arrhythmias play a prominent role.
Additionally, cardiomyopathy, which refers to a disease of the heart muscle, can also predispose individuals to SCA. This condition affects the heart’s size, shape, and structure, impairing its ability to pump blood efficiently. This condition can result in ischemia, potentially leading to fatal arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
Apart from these medical conditions, certain lifestyle factors may exacerbate the risk of SCA. Smoking is one of the most substantial contributors, as it is associated with various cardiovascular diseases that can result in SCA.
Understanding these causes is vital for prevention and management. Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions should be aware of their health and take preventive measures to mitigate the risk factors associated with SCA. Making lifestyle changes could substantially impact heart health and reduce the likelihood of succumbing to such catastrophic events.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is a medical emergency that can occur unexpectedly, and recognizing its symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. Identifying early warning signs may significantly increase the chances of survival and reduce the risk of severe complications. Individuals may experience sensations ranging from tightness or pressure to sharp, stabbing pain in the chest.
Another significant warning sign is shortness of breath. This symptom can manifest during physical activity or even at rest, indicating an underlying heart issue. Affected individuals may find it increasingly challenging to breathe, which might be accompanied by a feeling of impending doom or anxiety. It is essential to take these indicators seriously, as they can precede a critical cardiac event.
Fainting, or syncope, is another important symptom to monitor. Although fainting can occur for various reasons, when it happens in conjunction with other signs such as chest pain or shortness of breath, it can be a potential precursor to SCA. In some cases, this may precede a sudden cardiac event.
Recognizing these early warning signs—chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting—can be life-saving. Prompt medical attention is essential when these symptoms arise. The urgency in addressing detected signs can greatly influence the outcomes associated with Sudden Cardiac Arrest.
Understanding the demographic groups more susceptible to sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is crucial for early intervention and prevention. Certain factors contribute to an individual’s likelihood of experiencing this life-threatening event. Age is a significant consideration; the risk of SCA increases notably with advancing age. Individuals aged 45 and older, particularly men, are at a higher risk, though women may be more affected post-menopause due to hormonal changes that impact heart health.
Gender also plays a role in susceptibility to sudden cardiac arrest. However, this trend changes with age, as women catch up to men in risk profiles following menopause. Family history is another critical factor.
Pre-existing medical conditions significantly impact the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia can elevate the likelihood of fatal arrhythmias, particularly in conjunction with other risk factors.
Assessing personal risk factors is essential for understanding one’s potential susceptibility to sudden cardiac arrest.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) presents a formidable threat to life, as it leads to the abrupt cessation of heart function, resulting in the immediate loss of consciousness and cessation of breathing. In such critical situations, the initial moments following the event are crucial for the likelihood of survival. The response time of bystanders and the effectiveness of interventions like Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) play a pivotal role in determining the outcome of a victim experiencing SCA.
The first action that should be taken is calling emergency services. While waiting for help to arrive, bystanders should prioritize initiating CPR. Studies indicate that when CPR is delivered within the first few minutes, the survival rate significantly increases; in fact, immediate CPR can double or triple the chances of survival until advanced medical care is available.
Moreover, it is essential to remember that SCA can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. Therefore, training in CPR for the general public is paramount. By doing so, the likelihood of surviving this life-threatening emergency increases exponentially.
By calling for emergency assistance and initiating CPR without delay, bystanders not only contribute to the immediate care of someone suffering from SCA, but they also enhance that individual’s chances of recovery and long-term survival. This collective effort underscores the need for awareness, training, and preparedness within our communities.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is a critical medical emergency that requires immediate intervention. The treatment options available can significantly influence a patient’s prognosis and long-term heart health. One of the most vital tools in the management of SCA is the automated external defibrillator (AED). The widespread availability of AEDs in public spaces has been instrumental in enhancing survival rates.
In cases where the patient receives advanced medical care, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols are initiated. ACLS involves a series of life-saving procedures, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), airway management, and advanced medications. A healthcare provider’s timely response can stabilize the patient until further treatment is available.
Long-term interventions are also critical for patients who survive an episode of SCA. The use of ICDs has been shown to reduce mortality in high-risk populations.
Moreover, lifestyle modifications play a significant role in preventing recurrences of SCA. Patients are often advised to incorporate healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and smoking cessation into their daily routines.
In conclusion, the treatment options for sudden cardiac arrest encompass immediate and long-term strategies. The availability of AEDs, the use of ACLS protocols, the implementation of ICDs, and lifestyle modifications are all vital components in managing this life-threatening condition effectively. As awareness and education improve surrounding SCA, early intervention remains crucial for enhancing patient outcomes.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) poses significant risks; however, individuals can adopt various proactive measures to mitigate these risks effectively. One of the fundamental strategies includes maintaining a healthy diet, abundant in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Regular exercise plays a critical role in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, including SCA. Engaging in physical activities for at least 150 minutes each week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can strengthen the heart muscle, improve circulation, and enhance overall cardiovascular fitness. Exercise has the added benefit of reducing stress levels, which is another crucial factor in heart health.
Effective stress management is vital for maintaining a healthy heart. Establishing a balanced work-life dynamic and ensuring sufficient sleep can also contribute significantly to stress reduction.
Avoiding harmful habits, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, is paramount. Individuals are encouraged to seek support to quit smoking and to moderate their alcohol consumption in line with recommended guidelines.
Lastly, regular screenings and consultations with healthcare professionals are crucial for early detection and management of risk factors associated with SCA. By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly decrease their risk of experiencing sudden cardiac arrest.
Understanding sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is crucial in fostering a society prepared to respond effectively during emergencies. Public awareness and education play a vital role in equipping individuals with the knowledge required to act confidently when faced with such life-threatening situations. Community initiatives that focus on teaching cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs) can significantly enhance survival rates in cases of SCA.
Therefore, understanding the correct technique and the importance of timing is essential. Community programs often hold training sessions that allow individuals to practice CPR skills, increasing the likelihood that bystanders will respond swiftly and effectively in an emergency. Knowing how to use an AED can be a decisive factor in saving a life.
Moreover, educational campaigns can raise awareness about the risk factors associated with sudden cardiac arrest, encouraging individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles that may decrease their susceptibility to cardiovascular issues. Organizations can collaborate with schools, workplaces, and various community groups to incorporate training and awareness programs into their outreach efforts. By creating a culture of preparedness, communities can improve response times and outcomes for those affected by SCA.
In conclusion, fostering awareness and education surrounding sudden cardiac arrest is imperative. Through community programs that teach vital skills like CPR and AED usage, we can empower individuals to take action during emergencies, ultimately saving lives and decreasing the impact of this serious health threat.
Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) remains a critical health issue, representing a significant cause of mortality in various populations. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments associated with SCA is imperative for fostering a well-informed community. Throughout this article, we have outlined that SCA can occur unexpectedly, often stemming from underlying heart conditions, and may present with limited warning signs. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for prompt action—a delay could mean the difference between life and death.
Education plays a pivotal role in combating the unpredictability of sudden cardiac arrest. Initiatives that promote awareness of heart health, including regular medical check-ups and lifestyle modifications, are essential.
Collective awareness and preparedness can lead to timely interventions that significantly improve prognosis and save lives.
Ultimately, raising awareness about sudden cardiac arrest is a shared responsibility.