We envision a world where everyone has the tools and knowledge to live a balanced, healthy, and fulfilling life. By providing reliable resources, personalized programs, and community support, we aim to be a beacon of hope for those on their health journey.
Table of Contents
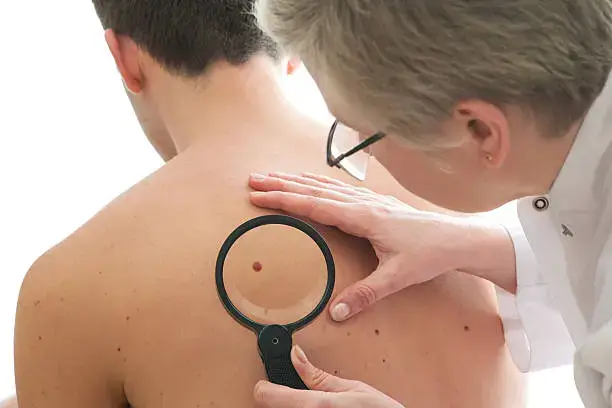
What is Nodular Melanoma?

Nodular melanoma is a specific type of skin cancer that is classified as one of the most aggressive forms of melanoma. Unlike other types of melanoma, which may develop from existing moles or skin lesions, nodular melanoma typically appears de novo, meaning it arises without any pre-existing conditions. This characteristic makes it particularly dangerous, as it often goes undetected in its early stages, melanoma of skin cancer get info; allowing for rapid progression.
This type of melanoma generally presents as a dark, elevated nodule on the skin, often varying in color from brown to black, and may sometimes exhibit shades of red, blue, or white. The key distinguishing feature of nodular melanoma is its vertical growth and tendency to invade deeper layers of the skin more quickly than other melanoma types. This aggressive growth pattern often leads to an increased likelihood of metastasis, or the spread of cancer to other parts of the body, compared to other melanoma varieties.
The prevalence of nodular melanoma has been a growing concern in dermatology and oncology. It accounts for approximately 15-30% of all melanoma cases and is particularly common among older adults, though it can affect individuals of any age. The 5-year survival rate for nodular melanoma can be significantly lower than that of other melanomas, emphasizing the importance of early detection and intervention. Regular skin checks and awareness of new growths, especially those that change in size or color, are crucial for timely diagnosis.
In summary, nodular melanoma represents a critical focus in skin cancer research and treatment due to its aggressive nature, rapid growth, and distinct clinical characteristics. Understanding this type of melanoma is essential for effective prevention and early detection strategies.
Symptoms and Signs of Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma is a type of skin cancer that is recognized for its distinctive nodular lesions, which can present with various symptoms and signs that require careful observation. One of the hallmark characteristics of nodular melanoma is the appearance of a raised, dome-shaped nodule that often feels firm to the touch. These nodules typically emerge suddenly, distinguishing them from other types of melanoma that may develop more gradually. As the nodules grow, they may change in color, often presenting shades of black, brown, or even red, which can be alarming if noticed during self-examinations.
Another significant sign is the alteration in texture of the lesion. Nodules may appear smooth, but as they progress, they can become scaly or ulcerated, signifying a more advanced state of the melanoma. Some patients may experience itching or tenderness around the nodule, which could indicate that medical attention is needed. It is crucial to perform regular self-checks on areas prone to sun exposure, such as the arms, legs, back, and face, where nodular melanoma is frequently found. The mnemonic ABCDE (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolving) can be helpful in identifying suspicious lesions.
Early detection is vital in managing nodular melanoma effectively, as timely intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes. Consulting a dermatologist for any concerning changes in the skin is recommended. Healthcare professionals are equipped to provide thorough examinations and may perform a biopsy for a definitive diagnosis. Awareness of the symptoms and signs helps promote proactive health measures and facilitates early intervention, thereby increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors

Nodular melanoma is a particularly aggressive form of skin cancer characterized by its rapid growth and tendency to invade surrounding tissues. Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors associated with this condition is crucial for early detection and intervention. One of the primary influences on the development of nodular melanoma is genetic predisposition. Individuals with a family history of melanoma or other skin cancers are at a heightened risk. Certain genetic mutations, particularly in the CDKN2A and BRAF genes, have been associated with an increased likelihood of developing melanoma, including the nodular type.
Environmental factors play a significant role in the onset of nodular melanoma as well. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is one of the most critical risk factors; both natural sunlight and artificial sources, such as tanning beds, contribute to skin damage and the potential for malignant changes. Excessive exposure to UV radiation alters the DNA in skin cells, which can lead to skin cancer. This risk is further magnified in individuals with fair skin, light hair, and a predisposition to sunburn, as these traits indicate lower melanin production and, consequently, less natural protection against UV damage.
Other lifestyle factors may also elevate the risk of developing nodular melanoma. For instance, individuals who have suffered from severe sunburns, especially during childhood, are at an increased risk. Additionally, age is a notable factor, as the likelihood of melanoma increases with advancing age. Individuals over the age of 50 are particularly vulnerable. Furthermore, immunosuppression caused by certain medications, transplant surgeries, or conditions like HIV can also contribute to the risk of developing this skin cancer. Awareness of these causes and risk factors is vital for proactive monitoring and prevention strategies.
Diagnosis of Nodular Melanoma
The diagnosis of nodular melanoma, a particularly aggressive form of skin cancer, begins with a careful visual examination by a healthcare professional. Dermatologists are skilled in identifying potential indicators of skin malignancies, including nodular melanoma. They assess the skin for asymmetrical moles, irregular borders, and variations in color, particularly focusing on newly developed growths or changes in existing moles. The ABCDE method—Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter greater than 6 mm, and Evolution over time—is a fundamental guideline employed during the examination process.
Once a suspicious lesion is identified, a biopsy is critical for definitive diagnosis. There are several biopsy methods available. The most common include punch biopsy, shave biopsy, and excisional biopsy. A punch biopsy involves removing a cylindrical core of skin, while a shave biopsy removes the outer layers of skin and allows for quicker analysis. In cases where complete removal is possible and necessary, an excisional biopsy may be performed, where the entire lesion and some surrounding tissue are excised. Each method has its indications, and the choice often depends on the size and location of the suspected nodular melanoma.
In addition to biopsy, imaging tests may also play a vital role in the diagnosis and staging of nodular melanoma, especially if there is suspicion of metastasis. Techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI may be utilized to evaluate whether cancer has spread beyond the initial site. Early and accurate diagnosis of nodular melanoma is crucial, as it significantly improves treatment outcomes. With a timely diagnosis, healthcare providers can initiate appropriate interventions, thereby enhancing the chances of remission and survival for patients affected by this aggressive skin cancer.
Stages of Nodular Melanoma

Nodular melanoma is a particularly aggressive form of skin cancer that is characterized by its rapid growth and tendency to metastasize. The classification of nodular melanoma into various stages is crucial in determining appropriate treatment options and the overall prognosis for the patient. Clinically, the stages are categorized using the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system, which assesses the extent of the disease based on tumor size, lymph node involvement, and the presence of distant metastases.
The earliest stage is known as Stage 0, or in situ melanoma, where the cancerous cells are confined to the epidermis and have not invaded deeper tissues. This stage often has an excellent prognosis with surgical excision being a standard treatment. As the disease progresses to Stage I, the melanoma may invade deeper layers of the skin but is still localized, presenting a favorable outcome with treatment options primarily focusing on surgical removal and, in some instances, sentinel lymph node biopsy.
In Stage II, the tumor is larger or thicker, and while still localized, there is a higher risk for recurrence and metastasis. Treatment may involve more extensive surgical intervention and possibly adjuvant therapies. Stage III indicates regional lymph node involvement, and the prognosis starts to diminish. Patients often require more aggressive management, which may include a combination of surgery, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy aimed at controlling the cancer’s progression.
Finally, Stage IV denotes metastatic cancer, where nodular melanoma has spread to distant organs or tissues. The treatment options become more complex and may incorporate systemic therapies to manage the disease. Understanding the staging process is essential for patients, as it influences treatment strategies and provides insights into expected outcomes. Consultation with healthcare professionals is crucial to navigate through the various stages and tailor an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options
Nodular melanoma, a more aggressive form of skin cancer, requires prompt and effective treatment options to enhance patient outcomes. The primary approach for managing this condition is surgical excision, which entails the removal of the melanoma along with a margin of healthy tissue. This technique aims to achieve clear margins, thereby minimizing the risk of recurrence. The depth and spread of the melanoma significantly influences the extent of the surgical intervention. In early-stage nodular melanoma, a localized excision may suffice, whereas more advanced cases may necessitate lymph node involvement and additional interventions.
In certain scenarios where surgical excision is not feasible, radiation therapy can be employed as an alternative. While it is not the first line of treatment for nodular melanoma, it may be considered, especially for patients with unresectable tumors or those who have experienced a recurrence after initial surgery. Radiation therapy works by targeting cancer cells with high-energy rays, effectively shrinking tumors and alleviating symptoms.
Beyond these local treatments, systemic therapies are crucial in addressing more advanced stages of nodular melanoma. Immunotherapy has emerged as an innovative treatment option that harnesses the body’s immune system to combat cancer cells. Agents such as checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in significantly prolonging survival rates. Additionally, targeted therapy—using drugs that specifically target genetic mutations associated with melanoma—offers an effective strategy for managing this disease, particularly in patients with BRAF mutations.
It is essential to recognize that treatment plans for nodular melanoma should be highly individualized. Factors such as the stage of the melanoma, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences play a critical role in determining the best course of action. Therefore, a multidisciplinary approach involving dermatologists, oncologists, and other healthcare professionals is vital for the effective management of nodular melanoma.
Living with Nodular Melanoma
Receiving a diagnosis of nodular melanoma can be a life-altering experience that impacts one’s emotional and psychological well-being. Patients frequently navigate a range of feelings, including anxiety, fear, and uncertainty about the future. Understanding these emotional responses is crucial in managing the condition effectively. It is essential for individuals to acknowledge their feelings and seek help when needed, as this can significantly aid in the coping process.
Coping strategies play a vital role in managing the psychological impact of nodular melanoma. Engaging in supportive communities, whether in-person or online, allows individuals to share their experiences and gain insights from others who understand their journey. Support groups provide not only a sense of belonging but also opportunities to learn effective coping techniques. Furthermore, engaging in mindfulness practices and regular physical activity can reduce stress and improve mental health. Such strategies aid in fostering resilience while facing the challenges that accompany a melanoma diagnosis.
Additionally, the importance of ongoing monitoring and follow-up care cannot be overstated. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure that patients remain informed about their condition and any potential recurrence. This proactive approach not only fosters a sense of control but also enhances emotional well-being, as individuals are better prepared to navigate any changes in their health status. Furthermore, establishing a strong support system through family and friends can enhance one’s capacity to cope with treatment side effects and emotional strain.
Overall, living with nodular melanoma entails a multifaceted approach that incorporates emotional support, coping strategies, and consistent monitoring. By prioritizing mental health alongside physical wellness, individuals can enhance their quality of life and navigate their journey with a sense of empowerment.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing nodular melanoma involves a combination of proactive measures aimed at reducing exposure to risk factors and promoting early detection. One of the most effective methods to lower the risk of developing this aggressive skin cancer is through comprehensive sun protection strategies. It is essential to apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even on cloudy days, as ultraviolet (UV) rays can penetrate through clouds. Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating. Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, hats, and sunglasses, further enhances defense against harmful UV exposure.
In addition to routine sun protection, regular skin checks form a critical component of nodular melanoma prevention. Individuals should perform monthly self-examinations of their skin, looking for new moles or changes in existing moles. The ABCDE rule is particularly useful for this purpose: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variation, Diameter larger than 6mm, and Evolving characteristics are signs that warrant an immediate consultation with a healthcare professional. Establishing a habit of conducting these checks can help in the early identification of suspicious skin changes, which is vital, as early intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Furthermore, seeking medical advice for any concerning skin alterations is paramount. Dermatologists are trained to assess skin lesions accurately and can provide valuable guidance on further monitoring or necessary biopsies. Regular professional skin cancer screenings, particularly for individuals at higher risk due to factors like a family history of melanoma or a history of sunburns, can ensure an additional layer of precaution. Implementing these prevention strategies collectively reduces the likelihood of developing nodular melanoma while promoting overall skin health and awareness.
Conclusion: Empowerment through Knowledge
In our exploration of nodular melanoma, we have highlighted the critical aspects of this aggressive skin cancer subtype. Early detection is paramount, as it significantly influences treatment outcomes. Nodular melanoma typically manifests as a changing mole or lesion, often not exhibiting the same warning signs as other types of melanoma. Therefore, it is essential for individuals to be vigilant in monitoring their skin and recognizing any unusual changes that may occur.
We have also discussed the importance of understanding risk factors associated with nodular melanoma. These include genetic predispositions, ultraviolet exposure, and previous skin cancer history. By familiarizing themselves with these factors, individuals can better assess their own risk and take proactive steps towards prevention and early intervention. Engagement in regular skin checks, both self-examinations and professional evaluations, is advisable for early detection, which is essential for better prognosis and successful treatment.
Moreover, communication with healthcare professionals is vital. Individuals should feel empowered to voice their concerns regarding any skin changes to their dermatologists or primary healthcare providers. A collaborative approach not only enhances personal health management but also fosters trust in the healthcare system. Awareness of nodular melanoma and its characteristics can make a significant difference in outcomes, underscoring the necessity of education and vigilance in skincare.
Ultimately, by equipping ourselves with knowledge about nodular melanoma, we enhance our ability to protect our skin health effectively. Taking charge of one’s health, scheduling regular dermatological appointments, and maintaining a proactive attitude toward skin changes can minimize the risks associated with nodular melanoma. Knowledge is a vital tool in the fight against skin cancer, and each individual has the power to make informed decisions about their well-being.
blood work brain health cancer treatment climate health diabetes treatments digestive health disease management disease mapping exercise plan fitness tips hair care hair growth hair treatment health apps health foods health insurance health tips healthy habits healthy recipes heart disease home workouts immune boost immune foods keto plan keto recipes kidney disease lifestyle diseases meal delivery medicine innovation melanoma treatment mental health morning exercise natural remedies non melanoma nutritional advice nutrition assistance raw nutrition skin cancer skin care skin health sleep exercise sleep technology telemedicine services viral threats weight loss
Nodular Melanoma: A Comprehensive Guide to know now 1
Nodular melanoma is a specific type of skin cancer that is classified as one of the most aggressive forms of melanoma. Unlike other types of melanoma, which may develop from existing moles or skin lesions, nodular melanoma typically appears de novo, meaning it arises without any pre-existing conditions. This characteristic makes it particularly dangerous, as it often goes undetected in its early stages, melanoma of skin cancer get info; allowing for rapid progression.